Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a type of mood disorder. Bipolar disorder was called manic depression. in the past, and that term is still used by some people. It is a psychiatric illness that causes major disruptions in lifestyle and health.

Introduction
Everyone has occasional highs and lows in their moods. But people with bipolar disorder have extreme mood swings. They can go from feeling very sad, despairing, helpless, worthless, and hopeless (depression) to feeling as if they are on top of the world, hyperactive, creative, and grandiose (mania).
Types of Bipolar Disorder
- This disease is called bipolar disorder because the mood of a person with bipolar disorder can alternate between 2 completely opposite poles, euphoric happiness and extreme sadness.
- Symptoms of both mania and depression sometimes occur together, in what is called “mixed state.”
- The extremes of mood usually occur in cycles. In between these mood swings, people with bipolar disorder are able to function normally, hold a job, and have a normal family life. The episodes of mood swings tend to become closer together with age.
Symptoms

A person in the manic phase may feel indestructible, full of energy, and ready for anything. Other times that person may be irritable and ready to argue with anyone who tries to get in the way.
- Unrealistic plans, spending sprees, an increase in sexual affairs, or other reckless behavior, such as wild driving, also may occur.
- Less sleep and food than usual are needed.
- The person with mania can stay up all night but may find that not much was accomplished because he or she was easily distracted.
- The person with bipolar disorder may talk very quickly and jump from subject to subject. They often exhibit pressured speech during mania. Self-esteem may be inflated.

Although mania is said to alternate with depression, most people have more depressive episodes than manic ones.
- Sadness and crying spells are common.
- People who are depressed may not care enough to wash or comb their hair, change clothes, or even get out of bed in the morning.
- These people may sleep too much (hypersomnolence) or have difficulty getting to sleep (insomnia).
- Many of these people have no interest in food or have no appetite and lose weight. However, some eat excessively.
- People with depression have trouble thinking; they may forget to do important things such as paying bills because they feel so down.
- They withdraw from friends.
Causes
The development of drug addiction is multifaceted and can involve.
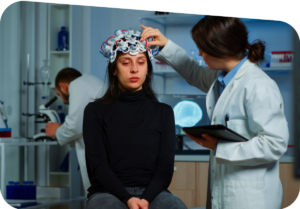
Bipolar disorder may result from a chemical imbalance within the brain. The brain's functions are controlled by chemicals called neurotransmitters.
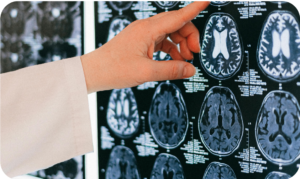
Other scientists believe that bipolar disorder may also be a result of premature death of brain cells that deal with mood and emotion. This causes the brain to lose control of mood.

Risk factors for bipolar disorder include the following: Most people never know why they develop bipolar disorder.
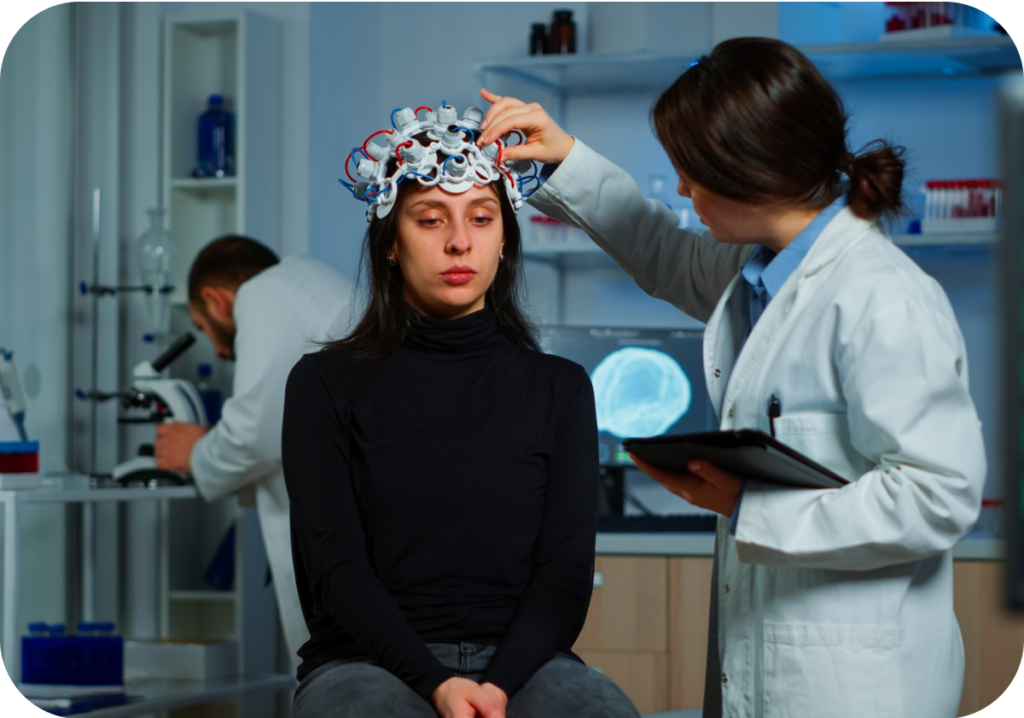
Bipolar disorder may result from a chemical imbalance within the brain. The brain's functions are controlled by chemicals called neurotransmitters.
Other scientists believe that bipolar disorder may also be a result of premature death of brain cells that deal with mood and emotion. This causes the brain to lose control of mood.

Risk factors for bipolar disorder include the following: Most people never know why they develop bipolar disorder.
Effects
Signs of depression.

Excessive worry
Excessive worry involves persistent & uncontrollable worrying about everyday things, even when there's little reason to.

Excessive guilt
Excessive guilt is a feeling of remorse or responsibility for something, whether real or imagined, that is often disproportionate to the actual event.

Sadness, crying spells
Sadness and crying spells are common human experiences, often triggered by loss, disappointment, or difficult life events.

Loss of energy
People with bipolar disorder may turn to drugs or alcohol to cope, increasing the risk of substance abuse.
Treatments
A variety of medications are available by prescription. These medications are usually referred to as mood stabilizers.
-
Many people start by taking lithium, which has been used for many years to treat bipolar disorder. Yet as many as half of all people with bipolar disorder do not respond to this medication.
Get Start With Easy Steps
Lithium
- The exact way lithium works in controlling the mood swings of bipolar disorder is unknown
- Lithium may take as long as 2 weeks to take full effect.
- It may have an “ant suicide effect.”
1


2
Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
- This medication reduces the excitability of brain cells and helps to control the symptoms of bipolar disorder.
- It is especially good for those who cycle between mania and depression very quickly.
Valproic acid (Depakote)
- This drug works for bipolar disorder by controlling abnormal electrical activity in the brain that may cause mood swings.
- This medication can be used alone or in combination with another medication.
- Blood levels should be monitored.
3