Anxiety
Anxiety can be accompanied by a variety of physical symptoms. Most commonly, these symptoms are related to the heart, lungs, and nervous system. You may feel as if you are having a heart attack.

Introduction
Anxiety is a feeling of apprehension, Fear or worry. Some fears and worries are justified, Such as worry about a loved one. Anxiety may occur without a cause, or it may occur based on a real situation, but may be out of proportion to what would normally be expected. Severe anxiety can have a serious impact on daily life.
Symptoms

Separate and intense periods of fear or feelings of doom developing over a very short time frame 10 minutes—and associated with at least 4 of the following
- Palpitations
- Sweating
- Trembling
- Shortness of breath
- Sense of choking
- Chest pain
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- A feeling of being detached from the world (derealization)
- Fear of dying
- Numbness or tingling
- Chills or hot flushes.

Excessive and unrealistic worry over a period of at least 6 months associated with 3 of the following:
- Restlessness
- Easy fatigue
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
- Muscle tension
- Sleep disturbances.
Causes
Anxiety may be caused by a mental condition, a physical condition, the effects of drugs, or from a combination of these. The doctor’s initial task is to see if your anxiety is caused by a medical condition.
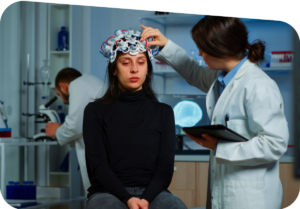
Panic disorder
In addition to anxiety, common symptoms of panic disorders are palpitations dizziness, and shortness of breath.

Generalized anxiety disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder is a mental health condition characterized by excessive, persistent.
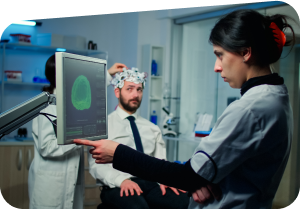
Phobic disorders
Phobic disorders are a type of anxiety disorder characterized by an intense, irrational fear of a specific object, situation, or place.
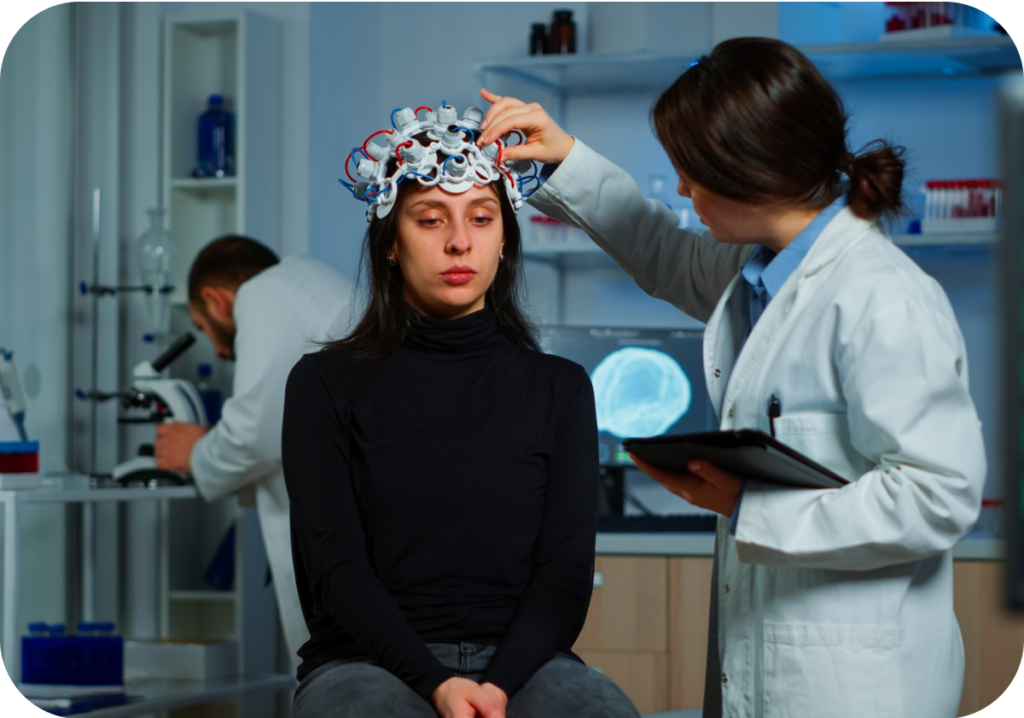
Panic disorder
In addition to anxiety, common symptoms of panic disorders are palpitations dizziness, and shortness of breath.

Generalized anxiety disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder is a mental health condition characterized by excessive, persistent.
Phobic disorders
Phobic disorders are a type of anxiety disorder characterized by an intense, irrational fear of a specific object, situation, or place.
Effects
Anxiety disorders can have profound impacts on an individual’s daily life, well-being, and relationships. Here are several key effects.

Impairs Daily
Functioning
People with anxiety may avoid daily activities like work, school, or social events due to fear.

Psychological Distress
Chronic anxiety often leads to co-occurring mental health issues, such as depression, exacerbating feelings of despair and hopelessness.

Reduced Quality of Life
The persistent nature of anxiety can diminish overall life satisfaction, affecting emotional well-being & making enjoyment of life’s activities difficult

Physical Health Impacts
Chronic anxiety can harm physical health, causing heart, gut, and immune problems.
Treatments
When the cause of anxiety is a physical ailment, treatment is directed toward eliminating that ailment. For example, if your thyroid gland were overactive and causing anxiety, the treatment might involve surgery and various thyroid-regulating medications.
Get Start With Easy Steps
Psychotherapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors.
Exposure Therapy: Gradual exposure to feared objects or situations.
1


2
Medications
Antidepressants (SSRIs, SNRIs): Commonly used to treat anxiety.
Benzodiazepines: Short-term relief; potential for dependence.
Lifestyle Changes
Regular exercise, stress management techniques, and healthy sleep patterns.
3


4
Support Groups
Community support for individuals coping with anxiety disorders.
Lifestyle Changes
Encouraging healthy habits such as regular exercise, nutrition, and mindfulness practices.
5