Depression
Clinical depression is not just grief or sadness. It is an illness that can challenge your ability to perform even routine daily activities. At its worst, depression may lead you to contemplate or commit suicide.

Introduction
Major depression is a change in mood that lasts for weeks or months. It is one of the most severe types of depression. It usually involves a low or irritable mood and/or a loss of interest or pleasure in usual activities. It interferes with one's normal functioning. A person may experience only one episode, but often there are repeated episodes over the lifetime. Dysthymia is less severe than major depression but usually goes on for a longer period, often several years.
Symptoms

You may be said to have clinical depression if you have a depressed mood for at least 2 weeks and have at least 5 of the following symptoms
- Feeling sad or blue
- Loss of interest or pleasure in usual activities Significant weight loss or weight gain
- Inability to sleep or excessive sleeping
- Agitation or irritability
- Fatigue or loss of energy
- Feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt
- Thoughts of death or suicide

- Children with depression also experience these classic symptoms, but may exhibit other symptoms as well, including the following:
- Poor school performance
- Persistent boredom
- Frequent complaints of physical problems such as headaches and stomachaches.
Some of the classic "adult" symptoms of depression may also be more obvious in children, such as change in eating or sleeping patterns.

While any of the classic symptoms of depression may occur in elderly people, other symptoms also may be noted.
- Diminished ability to think or concentrate
- Unexplained physical complaints (for example, abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, or muscle aches)
- Memory impairment (in about 10% with severe depression
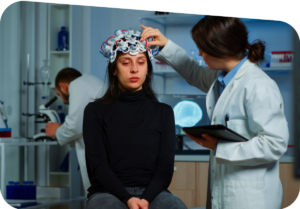
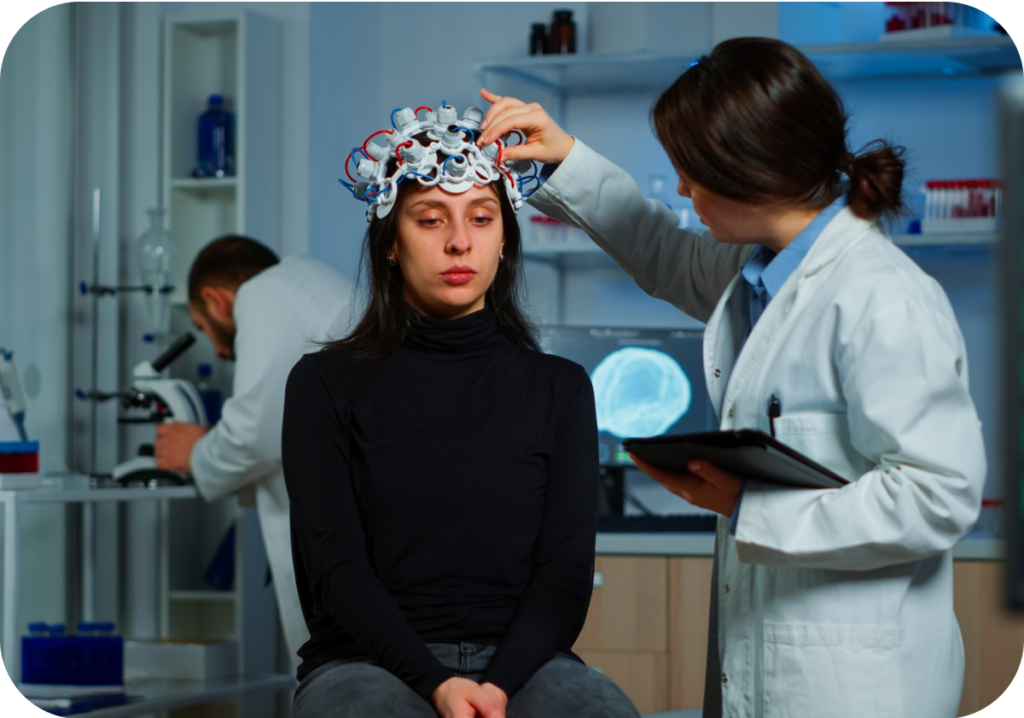
Causes
Depression is caused by a complex interplay of genetic, biological, environmental, and psychological factors. Some key aspects include.
Heredity
Certain types of depression seem to run in certain families. Research is ongoing as to exactly which genes are involved in depression.

Personality
People with certain personality traits are more likely to become depressed.

Situations
Difficult life events, loss, change, or persistent stress can cause neurotransmitters to become unbalanced, leading to depression.

Medical conditions
Depression is more likely to occur with certain medical conditions.
Heredity
Certain types of depression seem to run in certain families. Research is ongoing as to exactly which genes are involved in depression.

Personality
People with certain personality traits are more likely to become depressed.

Situations
Difficult life events, loss, change, or persistent stress can cause neurotransmitters to become unbalanced, leading to depression.

Medical conditions
Depression is more likely to occur with certain medical conditions.
Effects
Drug addiction can have severe negative impacts on individuals and their families, including.

Physical Health
Depression can affect appetite, leading to significant weight loss or gain.

Mental Health
Increased risk of anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders. Cognitive impairments affecting memory and decision-making.

Behavioral
People with depression may isolate themselves from friends and family.

Cognitive Effects
Trouble focusing, maintaining attention, or making decisions, even simple ones.
Treatments
Effective drug addiction treatment typically requires a combination of therapeutic interventions tailored to individual needs. Key components include.
Get Start With Easy Steps
Self-Care at Home
1


2
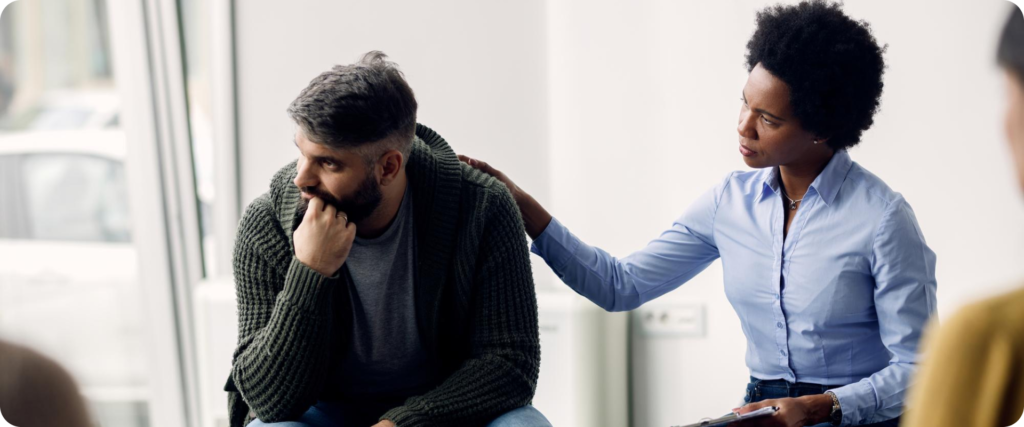
Focus on activities
- Try to identify and focus on activities that make you feel better. It is important to do things for yourself. Don’t isolate yourself. Take part in activities even when you may not want to. Such activity may actually make you feel better.
Lifestyle Changes
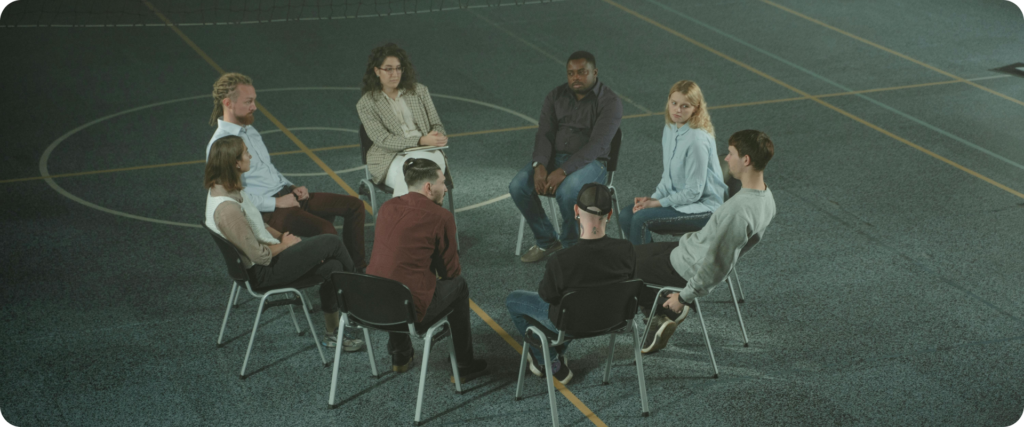
- Talk with your friends and family and consider joining a support group. Communicating and discussing your feelings is an integral part of your treatment and will help with your recovery
3


4
Support Groups
Try to maintain a positive outlook. Having a good attitude can be beneficial.
Regular Exercise
- Regular exercise and proper diet are essential to good health.
- Try to get enough rest and maintain a regular sleeping pattern.
- Avoid drinking alcohol or using any illicit substances.
5