Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
Depression as a mood disorder that affects how you feel, think, and handle daily activities.

Introduction
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. It's a common condition that affects children and adults.
Symptoms

People who are inattentive have a hard time keeping their mind on any one thing and may get bored with a task after only a few minutes. They may give effortless, automatic attention to activities and things they enjoy. But focusing deliberate, conscious attention to organizing and completing a task or learning something new is difficult.

People who are hyperactive always seem to be in motion. They can't sit still. Like Mark, they may dash around or talk incessantly. Sitting still through a lesson can be an impossible task. Hyperactive children squirm in their seat or roam around the room. Or they might wiggle their feet, touch everything, or noisily tap their pencil. Hyperactive teens and adults may feel intensely restless. They may be fidgety or, like Henry, they may try to do several things at once, bouncing around from one activity to the next.
Causes
Understandably, one of the first questions parents ask when they learn their child has an attention disorder is "Why? What went wrong?".
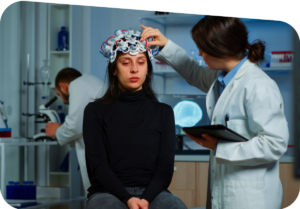
Health professionals
Health professionals stress that since no one knows what causes ADHD, it doesn't help parents to look backward to search for possible reasons.
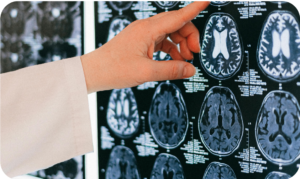
Biological
They are finding more and more evidence that ADHD does not stem from home environment, but from biological causes.

child's behavior
Knowing this can remove a huge burden of guilt from parents who might blame themselves for their child's behavior.
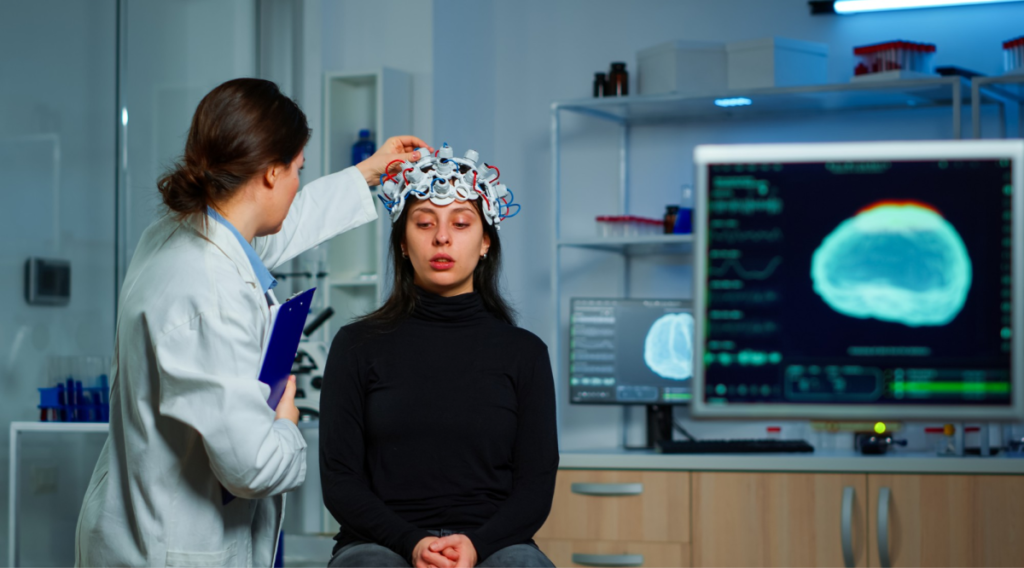
Health professionals
Health professionals stress that since no one knows what causes ADHD, it doesn't help parents to look backward to search for possible reasons.
Biological
They are finding more and more evidence that ADHD does not stem from home environment, but from biological causes.

child's behavior
Knowing this can remove a huge burden of guilt from parents who might blame themselves for their child's behavior.
Effects
ADHD can significantly affect many aspects of an individual’s life, leading to various challenges.

Academic Challenges
People with ADHD, young and old, often face challenges in school due to difficulty focusing.

Occupational Difficulties
Adults with ADHD may have trouble with work due to organizational and time management issues.

Strained Relationships
Impulsive behavior and difficulty focusing can lead to relationship problems and stress.

Low Self-Esteem
Frequent mistakes & perceived failures can lead to feelings of inadequacy & low self-esteem, affecting mental health & overall outlook on life.
Treatments
Effective drug addiction treatment typically requires a combination of therapeutic interventions tailored to individual needs. Key components include.
Get Start With Easy Steps
Ritalin
1


2
Medications
Lifestyle Management
Structure and routine, break tasks into manageable parts, and support educational adaptations.
3